请看题
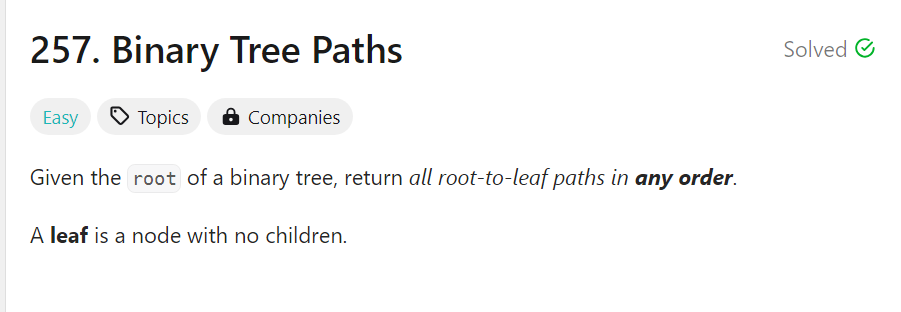
给一个二叉树结构的节点,要求输出内容为
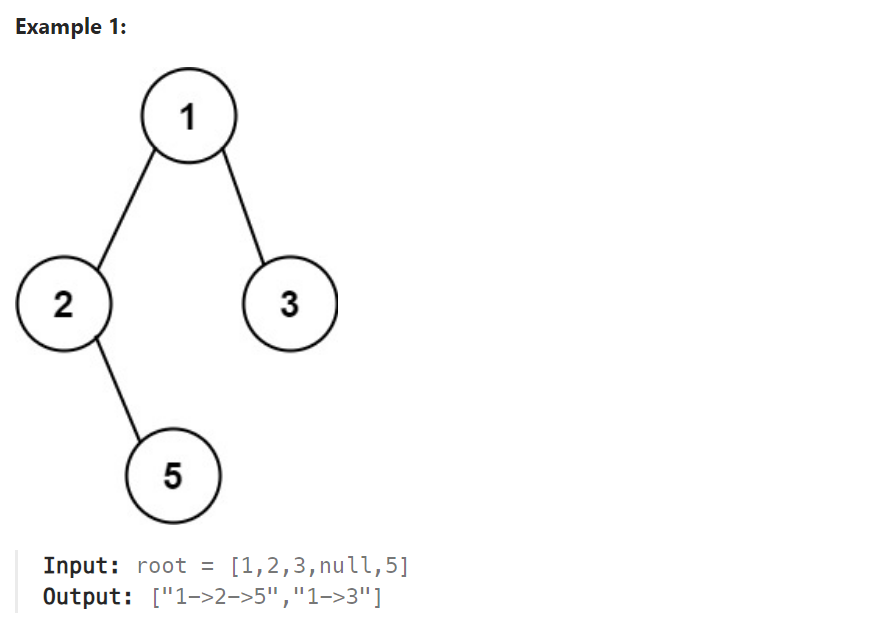
要求返回值为一个vector。
开始做题
先来看第二个Example。
一个树中只有一个节点,那么我们可以进行if判断来返回其节点,代码可为
1
2
3
4
| if(!node->left && !node->right)
{
ans.push_back(path);
}
|
想要理解代码,那就得先知道代码长什么样,此处为主函数用作解答
1
2
3
4
5
6
| vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root)
{
vector<string> ans;
dfs(ans, "", root);
return ans;
}
|
那么已经解决了Example 2 在上面的if,我们就可以进行针对其他的情况来进行解答了。
二叉树,无非就是递归,递归左节点,递归右节点,这里也是一样,在使用递归后,获取每一个节点的值,将其转为string然后push到vector中,当没有可以递归的节点后那么也就是该结束的时候,贴上递归结束条件代码
1
2
3
4
| if(!node)
{
return;
}
|
以上if和node != nullptr 等价
然后就是使用递归
1
2
| dfs(ans, path+"->", node->left);
dfs(ans, path+"->", node->right);
|
最后结束。
Code
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| /**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(vector<string> &ans, string path ,TreeNode *node)
{
if(!node)
{
return;
}
path += to_string(node->val);
if(!node->left && !node->right)
{
ans.push_back(path);
}
dfs(ans, path+"->", node->left);
dfs(ans, path+"->", node->right);
}
vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root)
{
vector<string> ans;
dfs(ans, "", root);
return ans;
}
};
|